Waste registration in Poland - key principles

Waste records are one of the most important elements of the waste management system in Poland. The obligations related to keeping records and preparing waste reports are precisely defined in the 2012 Waste Act. In this article, we will outline the key deadlines, the obligations of companies and the necessary information to be collected before preparing the report.
Contact for BDO registration and waste records
e.nadolna@ekologistyka24.pl , +48 881 045 376
j.blazewicz@ekologistyka24.pl , +48 500 867 153
Legal basis for waste recording in Poland
Keeping records of waste is primarily regulated by the Act of 14 December 2012. On waste (Journal of Laws 2013, item 21). It covers the principles of waste management, the responsibility of entities and administrative obligations. A key role is also played by the Database on Products and Packaging and Waste Management (BDO), which enables electronic record-keeping.
The overarching aim of the regulations is to protect the environment and promote a closed-loop economy. All data must be submitted in a timely manner and in accordance with the applicable regulations.
Who must keep records of waste?
Obligated entities
Waste records must be kept by all entities that generate, transport (in this case, the mandatory simplified accounting based on KPO), collect or process waste. This applies to both manufacturing and service businesses, including garages, restaurants or hospitals.
Importantly, this obligation also extends to farmers with farms of more than 75 ha. The exceptions are natural persons and organisational entities that are not entrepreneurs and that generate waste as part of their normal use.
Entry in BDO
Any entity required to keep waste records must be entered in the BDO register. Failure to register results in financial penalties of up to £1,000,000.
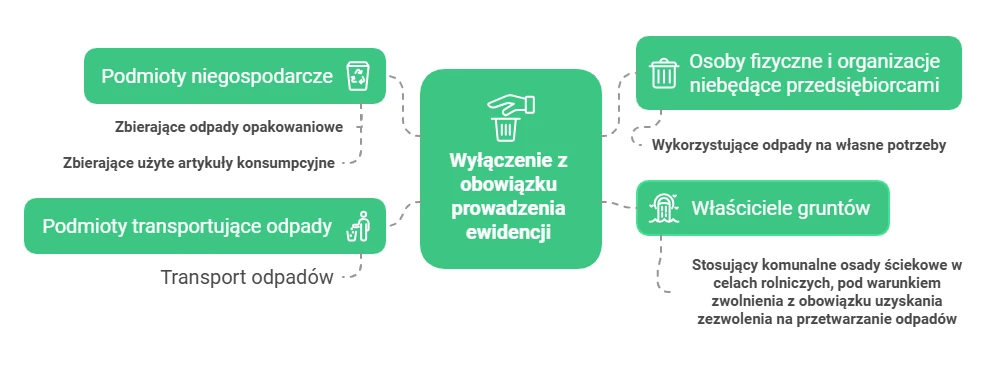
Waste records - who does not have to keep them?
- Individuals and organisations that are not businesses and that use waste for their own purposes.
- Owners of land on which municipal sewage sludge is applied for agricultural purposes, subject to an exemption from the waste treatment permit.
- Non-managers of the waste they collect:
- packaging waste,
- used consumer goods (e.g. medicines and drug packaging in pharmacies, used products in shops, waste in schools, offices and institutions).
- Operators transporting waste that they themselves have generated.
Deadlines for submission of reports
Key dates
Waste reports must be submitted no later than 15 March year following the reporting year. This applies to both generators and waste treatment operators. Companies generating hazardous waste often have to submit additional reports by the deadlines specified in their individual environmental permits.
What information do you need to gather before preparing your report?
Key data
- Waste type and code - according to the waste catalogue.
- Amount of waste generated - precise mass or volume data.
- Waste management methods - e.g. recycling, disposal, landfilling.
- Waste transport - data on those responsible for transport.
Data sources
It is important that you collect data systematically throughout the year. To this end, companies often use IT systems that allow the automatic generation of reports.
In summary, waste recording and reporting are key responsibilities that require precision, knowledge of the regulations and systematic action. Errors in this regard can lead to costly consequences, both financial and administrative.
If you think reporting is something too complicated or time-consuming, trust the professionals. By outsourcing, you'll focus on running your business with the confidence that your waste recording duties are in the best hands.
Contact with us today and keep your company safe.